MULIA288 merupakan link bandar judol resmi penyedia slot gacor terpercaya 2026 dan juga sebagai situs toto slot 777 yang sangat diminati oleh para sloters karena terbukti gampang menang maxwin hari ini.
Star Seller
Star Sellers have an outstanding track record for providing a great customer experience—they consistently earned 5-star reviews, shipped orders on time, and replied quickly to any messages they received.
You can only make an offer when buying a single item
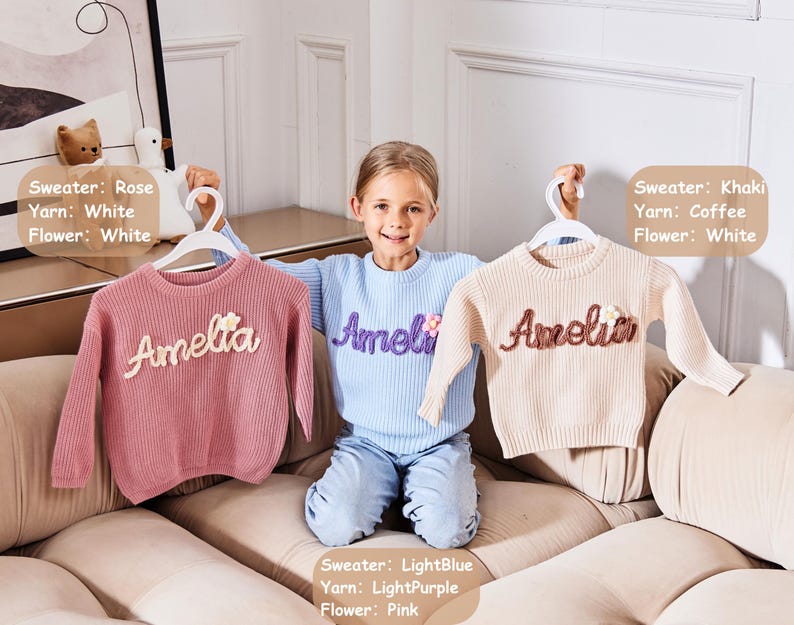
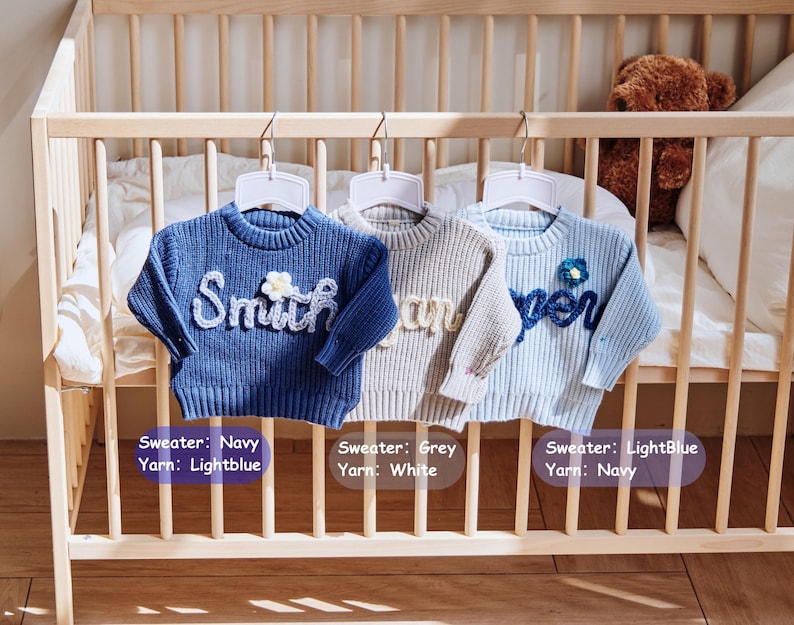
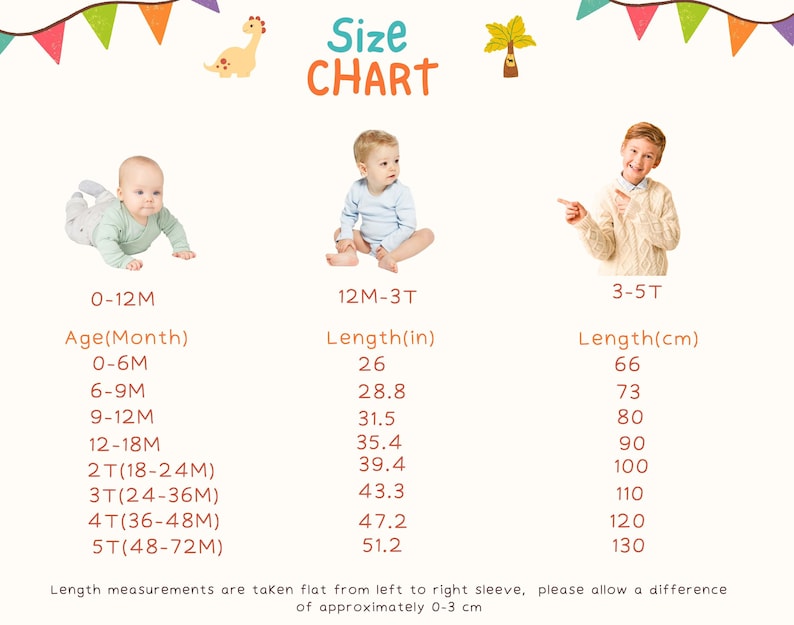
Penjelasan
-
Order today to get by Mar 29-Apr 4
Your order should arrive by this date if you buy today. To calculate an estimated delivery date you can count on, we look at things like the carrier's latest transit times, the seller's processing time and shipping history, and where the order is shipping to and from.
-
Returns & exchanges accepted within 30 days
Buyers are responsible for return shipping costs. If the item is not returned in its original condition, the buyer is responsible for any loss in value.
-
Cost to ship: USD 4.00
-
Ships from: United States
There was a problem calculating your shipping. Please try again.
Etsy Purchase Protection
Shop confidently on Etsy knowing if something goes wrong with an order, we've got your back for all eligible purchases — see program terms
Bandar Slot Gacor Rating Tertinggi
5 out of 5 starsMULIA288 itu gacornya stabil banget. Slot 777-nya sering kasih kemenangan besar dan proses WD-nya cepat. Bener-bener situs terpercaya!
Riko Simanjuntak Nov 16, 2025
Semenjak main di MULIA288, kemenangan terasa jauh lebih mudah. Banyak pilihan game gacor dan semuanya enak dimainkan. Recommended!
Sela Amelia Nov 15, 2025
Platformnya aman, ringan, dan fitur-fiturnya lengkap. Baru beberapa hari main aja sudah dapat maxwin. MULIA288 memang top!
Dany Setiawan Nov 16, 2025
Sebagai pemain setia slot 777, aku puas banget di MULIA288. Koleksi gamenya banyak, peluang menang besar, dan anti ribet.
Vira Zulfahira nov 16, 2025



























 Promo
Promo
 Login
Login
 Daftar
Daftar
 Live Chat
Live Chat